General
What is Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is on-demand access, via the internet ("the cloud"), to computing resources—applications, servers, data storage, development tools, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence and more—hosted at a remote data center managed by a cloud services provider to offer faster innovation, flexible resources, and economies of scale. The cloud services provider makes these resources available for a monthly/yearly subscription fee or bills them according to usage.
Compared to traditional on-premises IT, cloud computing brings the following benefits:
Lower IT costs: Cloud lets you offload some or most of the costs and effort of purchasing, installing, configuring, and managing your own on-premises system. You can avoid the upfront cost and complexity of owning and maintaining own IT infrastructure, and instead simply pay for what you need and use.
Improve agility and time-to-value: With cloud, companies can move faster on projects and test out concepts without lengthy procurement and big upfront costs. This concept of business agility is often mentioned by cloud advocates as a key benefit. Cloud also lets you empower certain users—specifically developers and data scientists—to help themselves to software and support infrastructure.
Scale more easily and cost-effectively: Cloud provides elasticity—instead of purchasing excess capacity that sits unused during slow periods, you can scale capacity up and down based on the spikes and dips in traffic. You can also take advantage of your cloud provider's global network to spread your applications closer to users around the world.
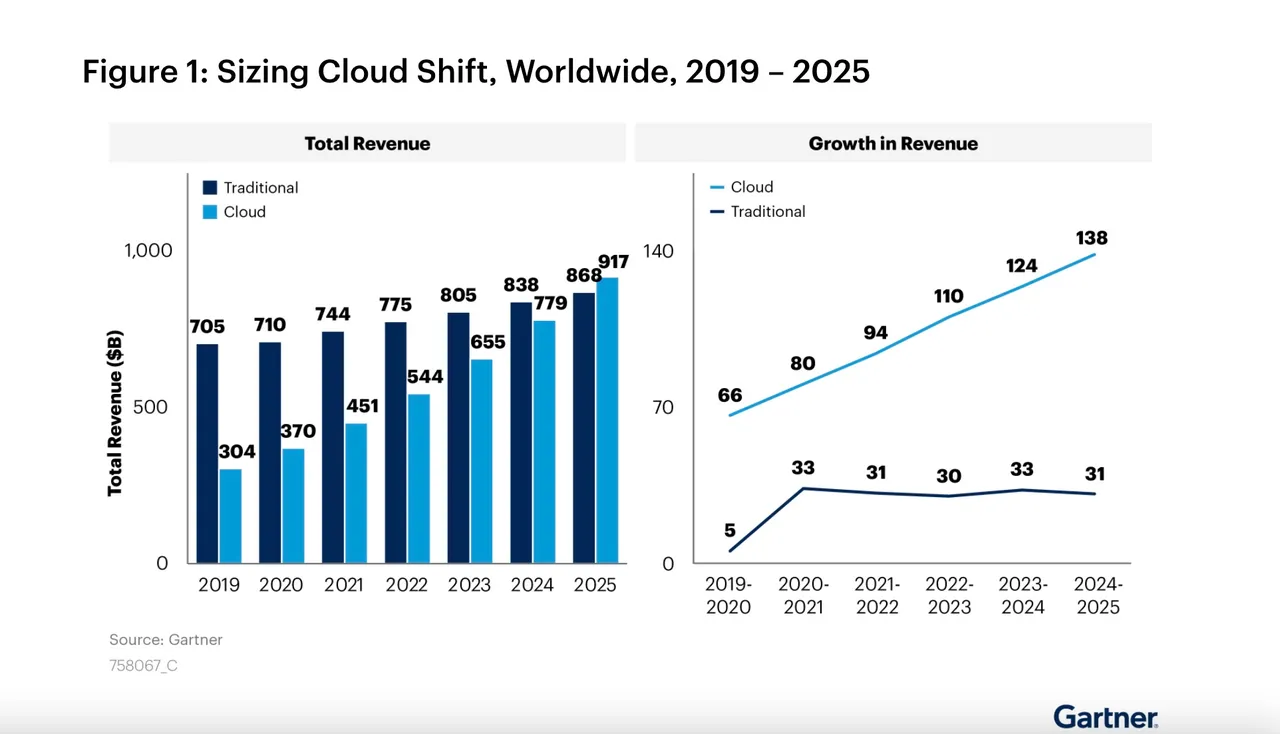
Image: Gartner
Tech analyst Gartner predicts that as much as half of spending across application software, infrastructure software, business process services and system infrastructure markets will have shifted to the cloud by 2025, up from 41% in 2022. It estimates that almost two-thirds of spending on application software will be via cloud computing, up from 57.7% in 2022.
According to Gartner, the demand for integration capabilities, agile work processes and composable architecture will drive the continued shift to the cloud.
Next topic: SaaS: Software as a Service
Previous topic: Documentation Home
Need help?
Connect with us
New to Xin 365?
Sign up today